Discover the Nucleic Acids Found in Animal Cells
Essential Components of Cellular Life
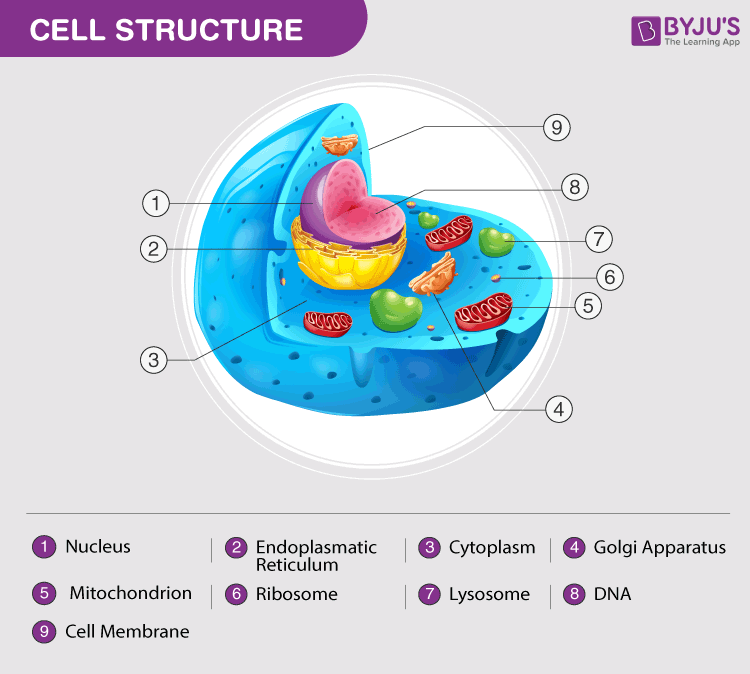
Within the intricate realm of animal cells, two vital nucleic acids play crucial roles in the transmission and processing of genetic information: Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA). These molecules serve as the blueprints of life, directing cellular processes and ensuring the continuity of genetic inheritance.
DNA's Role in Genetic Storage
DNA, the primary genetic material, resides within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, forming thread-like structures known as chromosomes. Each chromosome carries a specific set of genes, which are composed of DNA sequences that code for specific proteins. DNA's double-helix structure, with its complementary base pairs, provides a remarkably stable and reliable means of storing genetic information.
RNA's Role in Protein Synthesis
RNA, a versatile molecule, plays a multifaceted role in protein synthesis. One type of RNA, known as messenger RNA (mRNA), carries genetic information from the nucleus to ribosomes, the protein-making machinery of the cell. Transfer RNA (tRNA) also participates in protein synthesis by delivering specific amino acids to the ribosomes, enabling the assembly of proteins according to the genetic code.
Conclusion
DNA and RNA are indispensable nucleic acids that together constitute the foundation of cellular life. They work in concert to transmit genetic information, guide cellular processes, and ensure the continuation of life through generations.
Comments